🔹 What is ResNet (Residual Network)?
ResNet is a deep learning-based Convolutional Neural Network (CNN) model introduced by Microsoft Research in 2015. It was proposed in the paper "Deep Residual Learning for Image Recognition" and won 1st place in the ImageNet Challenge (ILSVRC 2015) with a significantly lower error rate than previous models.
📄 Paper Link: ResNet Paper (PDF)
1️⃣ Key Concept of ResNet
ResNet was developed to solve the vanishing gradient problem, which occurs when training deep networks.
Before ResNet, deeper networks often suffered from degradation problems, where adding more layers did not improve accuracy or even worsened performance.
ResNet introduced skip connections (shortcut connections) to allow the gradient to flow directly through the network, making very deep architectures trainable.
🔹 Main Features of ResNet
✅ Introduces residual learning to ease training in deep networks
✅ Uses skip connections (shortcut paths) to mitigate the vanishing gradient problem
✅ Can train ultra-deep networks (e.g., ResNet-50, ResNet-101, ResNet-152)
✅ Achieved state-of-the-art performance in the ImageNet challenge
2️⃣ ResNet Network Structure
ResNet is built using residual blocks, where a shortcut path directly connects the input to the output of a deeper layer.
🔹 Residual Block Formula
Instead of learning a function H(x) directly, ResNet models the function as:
H(x) = F(x) + x
H(x)=F(x)+x
where:
- F(x) is the residual function (the part the network learns).
- x is the original input (identity mapping).
- H(x) is the final output.
The shortcut connection allows the network to skip layers, making gradient backpropagation more effective and stabilizing training.
3️⃣ Advantages of ResNet
✔ Solves the vanishing gradient problem by using skip connections
✔ Enables training of very deep networks (50+ layers)
✔ Improves accuracy without significantly increasing computation
✔ Has become the foundation for many modern architectures (e.g., ResNeXt, DenseNet, EfficientNet)
4️⃣ Disadvantages of ResNet
❌ Computational cost increases as depth grows
❌ Shortcut connections do not always contribute equally to all layers
❌ Batch normalization is required for stable training
5️⃣ Applications of ResNet
ResNet is widely used in various computer vision tasks:
🔹 Image classification (e.g., ImageNet, CIFAR-10)
🔹 Object detection (e.g., Faster R-CNN, YOLO)
🔹 Semantic segmentation (e.g., U-Net, DeepLab)
🔹 Face recognition (e.g., ArcFace)
✅ Conclusion
ResNet revolutionized deep learning by making very deep networks trainable and efficient.
It remains one of the most widely used architectures in modern computer vision applications. 🚀
🔹 Additional Explanation
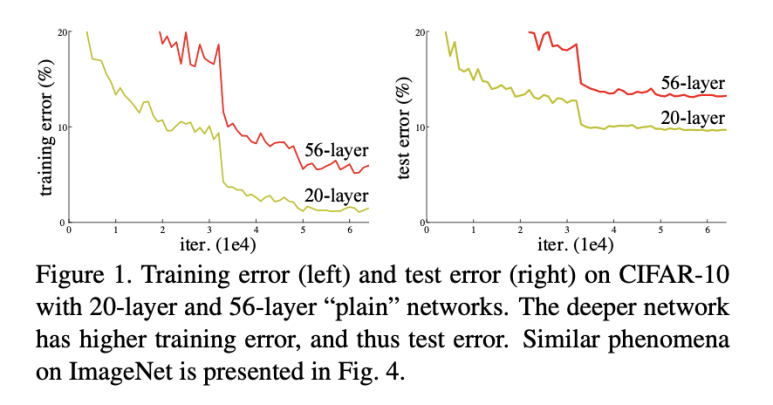
In traditional deep networks, as the number of layers increases, the gradient vanishing problem occurs, leading to a decrease in performance. This happens because the gradients obtained through backpropagation become either too small or too large, causing instability. Additionally, as the depth increases, test error also tends to rise.
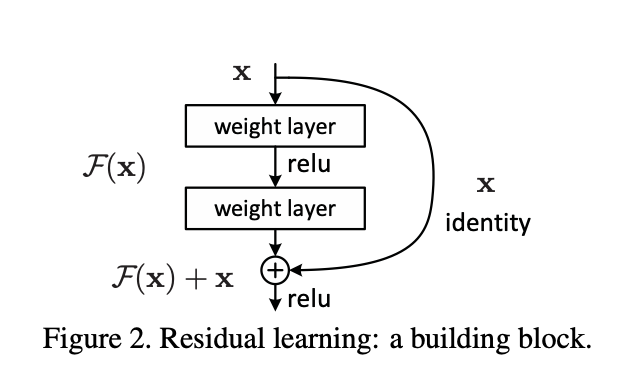
In Figure 2, the rounded x on the right represents the input. Previously, standard networks used only the output value for a given input. However, in ResNet, the input itself is carried forward and used in the computation. This structure is called a building block, where the function F(x) passes through weighted layers and is then added to the input x, forming the equation F(x) + x = H(x). This is known as Residual Mapping.
For reference:
Residual
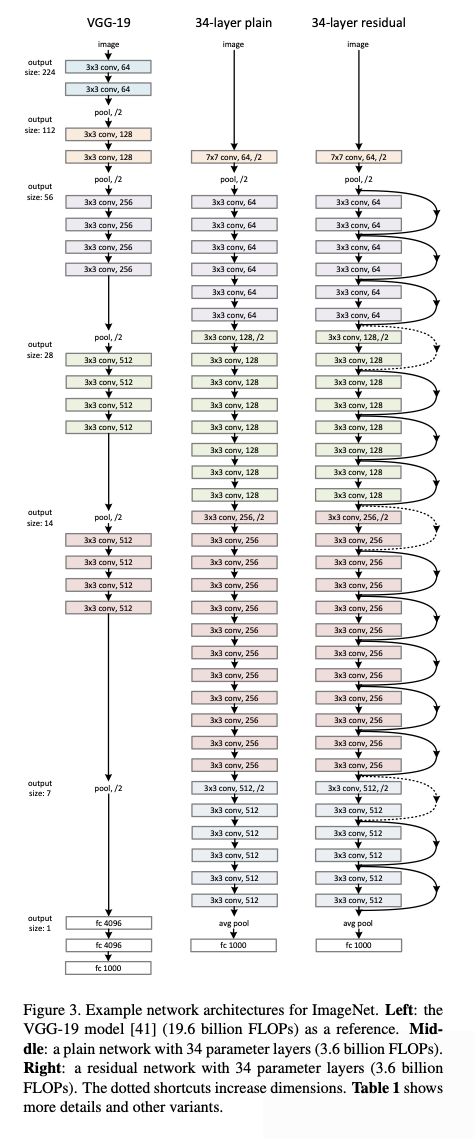
Residual=H(x)−x=F(x)The diagram compares VGG-19, a plain network, and a residual network, clearly showing that ResNet continuously carries residual mappings forward to the next layers.
Another key difference is that in the 34-layer ResNet, after the initial layers, it consistently uses 3×3 convolution layers. Additionally, whenever the feature map size is halved, the depth of the feature map is doubled.
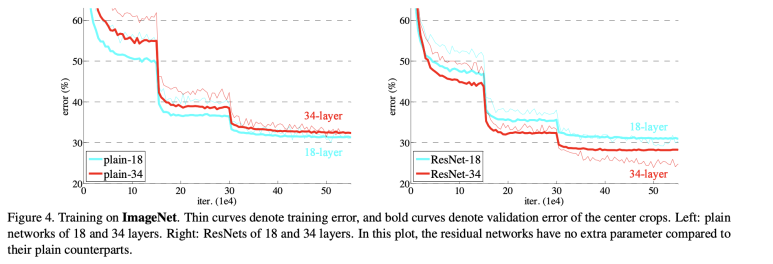
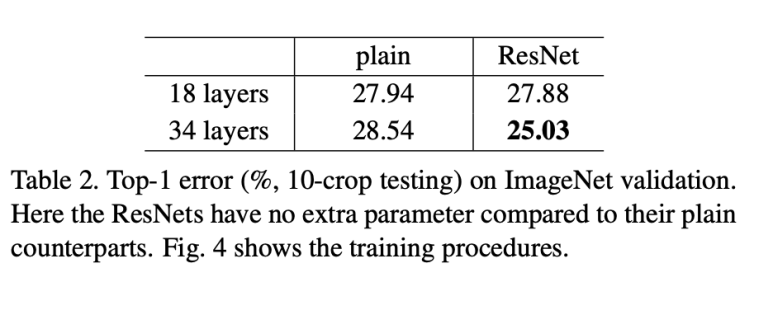
On the left side of the figure, in the plain network, deeper layers result in higher error rates. However, in ResNet, deeper networks actually achieve lower errors, demonstrating its effectiveness. 🚀